Ellison Technologies
Application
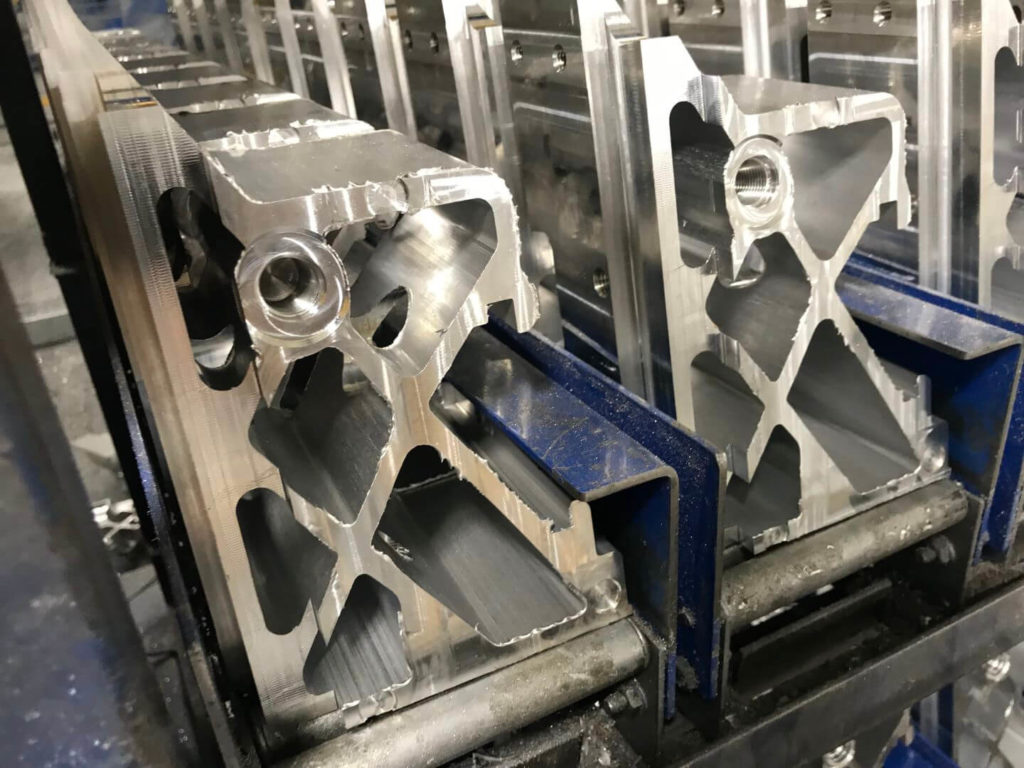
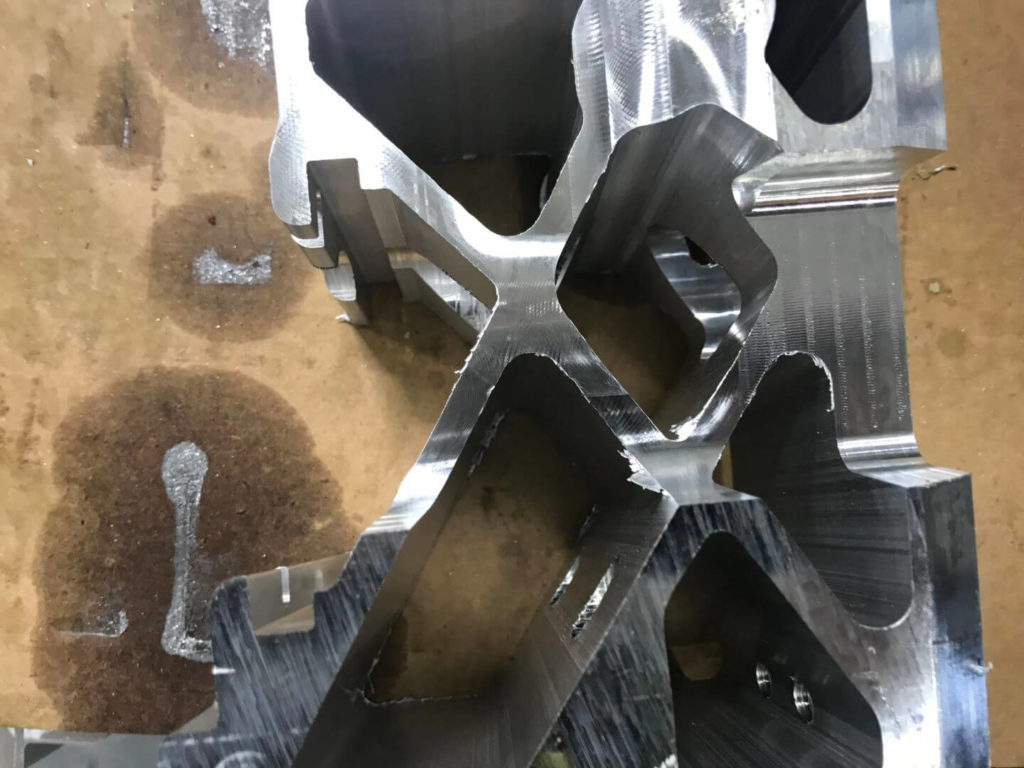
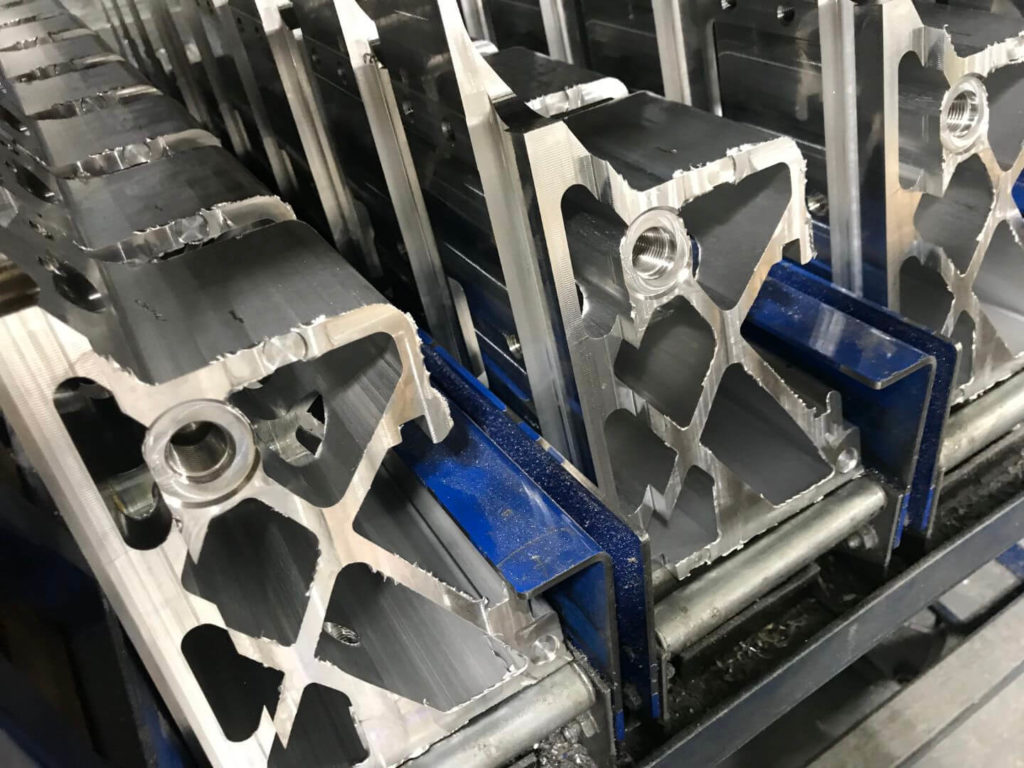
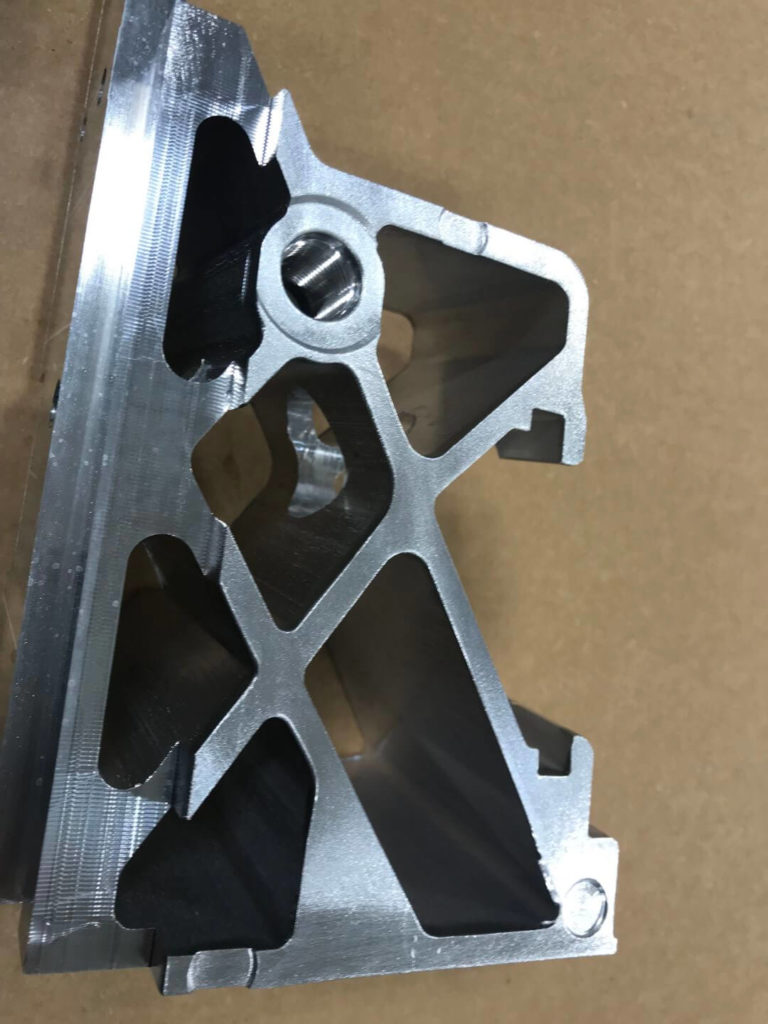
An automotive manufacturer required an autonomous solution for burrs created when machining aluminum bracketry. Burrs were located on inside and outside of extrusion edges and webbing. The customer specified no loose material could fall from these brackets post-deburr. This cell to was required to work in conjunction with a transportation cart system that was already in use at their facility. A large parts washer was needed to clean the parts post-deburr. All safety implementations required for an open cell of this magnitude were required.
Solution
Machine Base
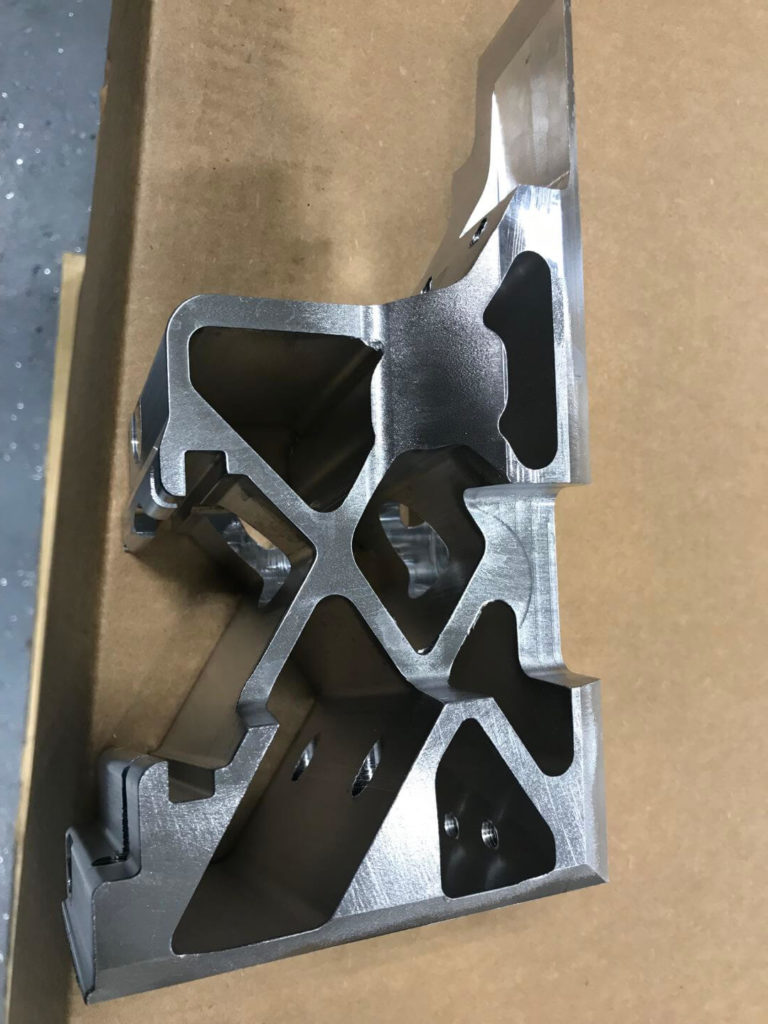
- The machine cell is made up of two mirrored stations to reflect the mirrored brackets to be deburred. Each work station consists of a ½” steel wall housing and 1” steel plate floor panel. Provisions are made so that base assemblies can be lagged to the floor.
Processing
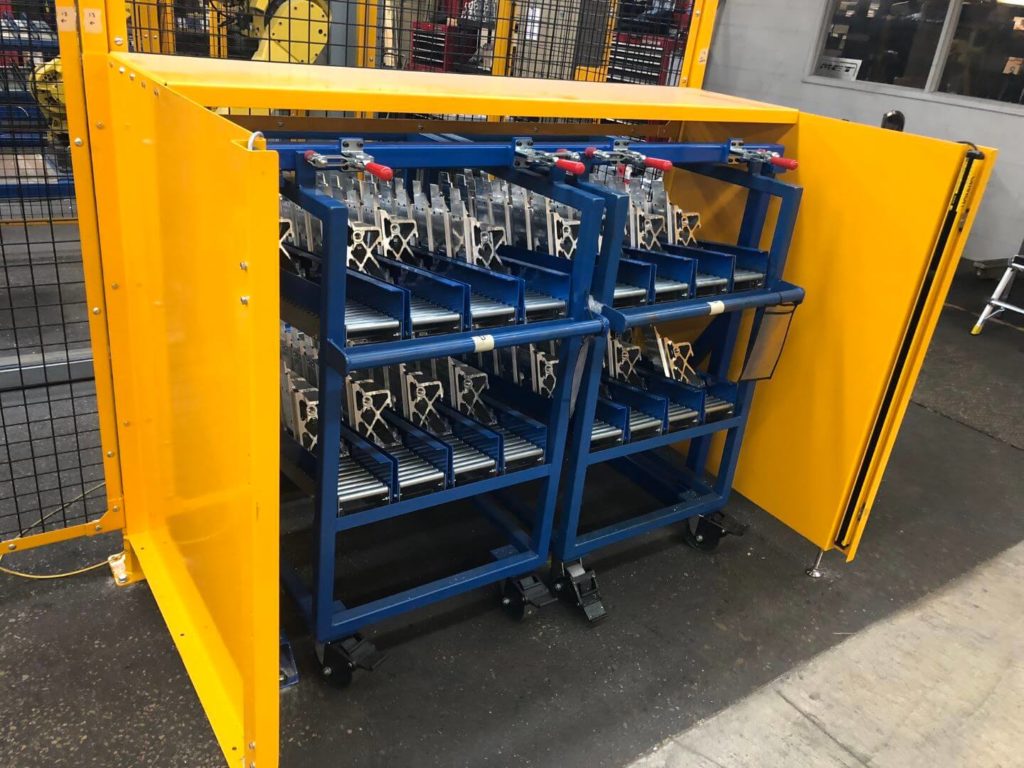
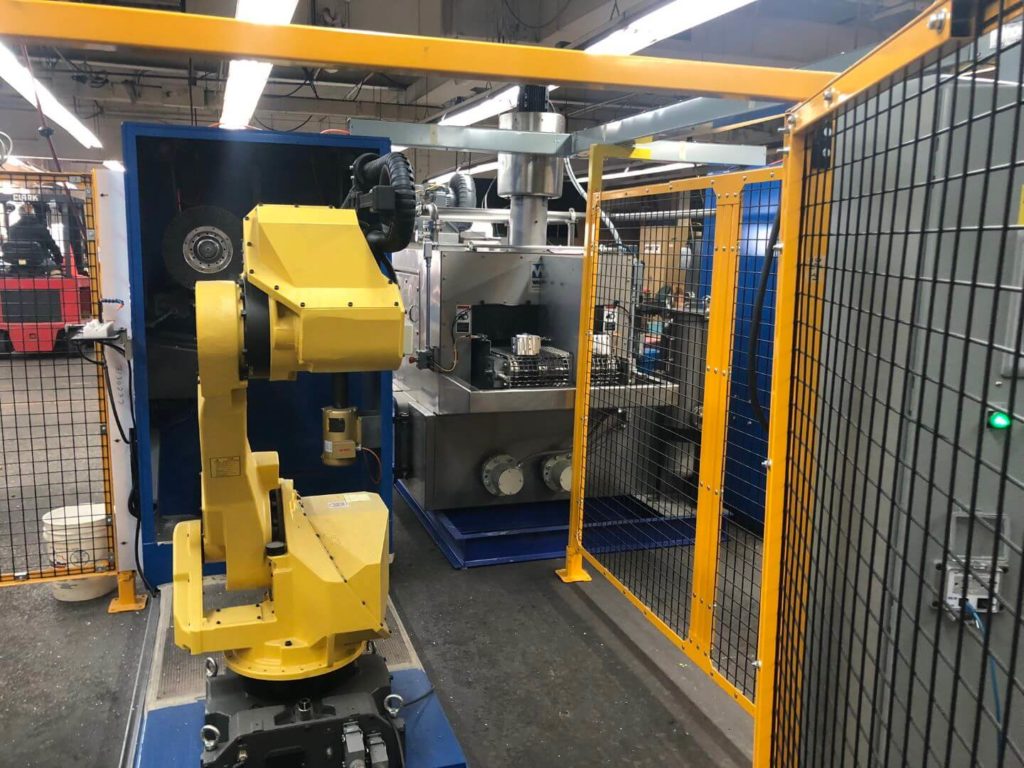
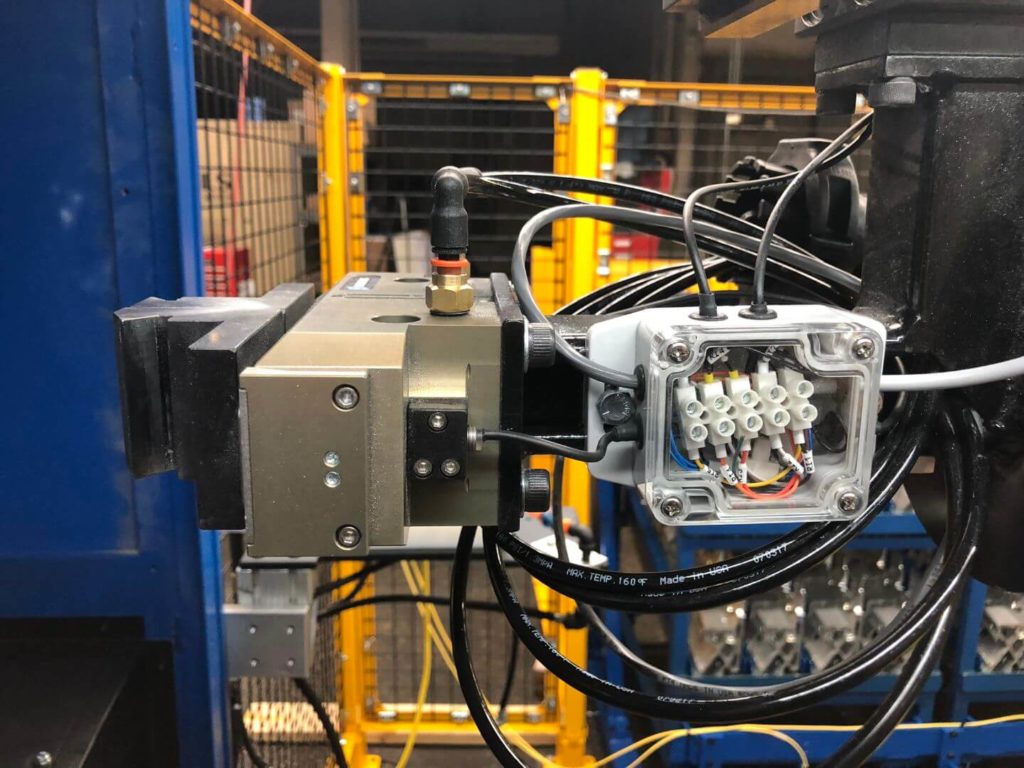
- Brackets are taken to a customer-manufactured docking station and locked into place. Each robot is equipped with custom “pick” End of Arm Tooling (EOAT). The robot’s EOAT consists of two pneumatically actuated grippers with custom clamp tooling. Air pressure to each gripper can be adjusted via precision regulator.
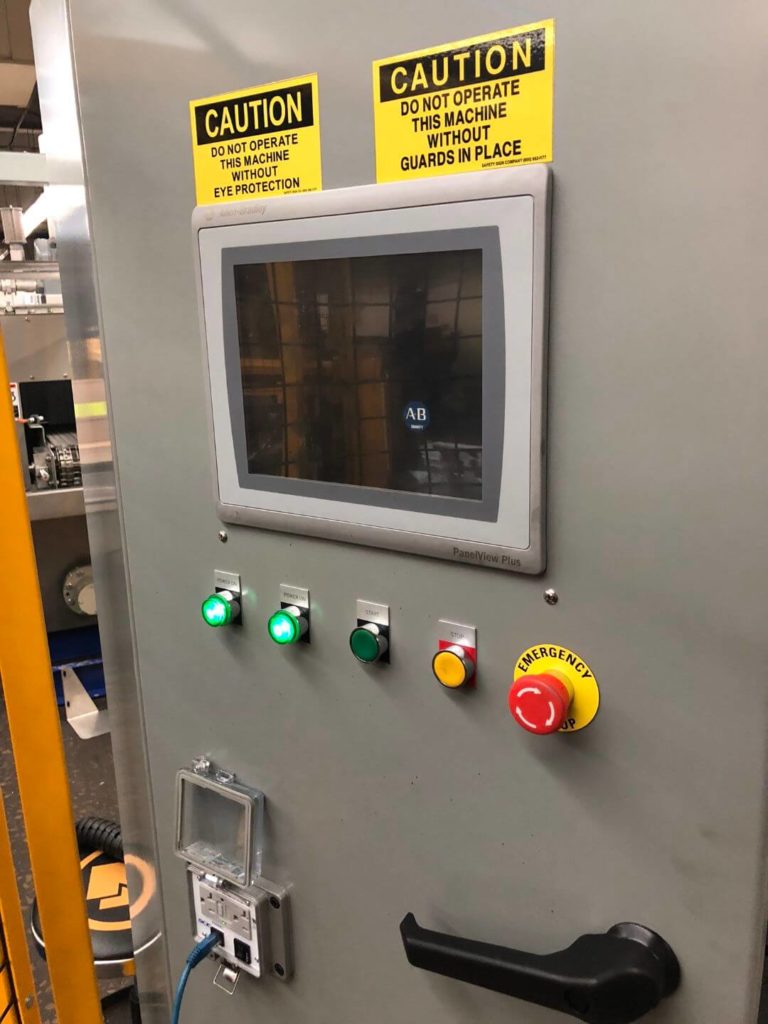
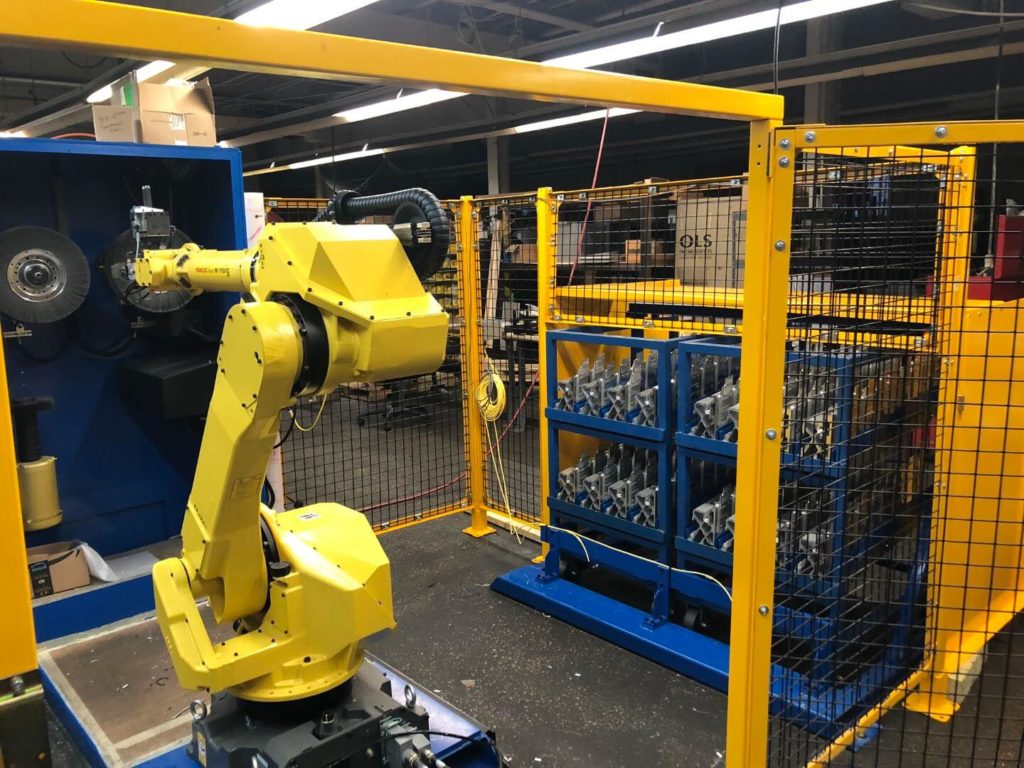
- Once the robot has been taught all cart positions by a CDMC robot programmer, it can load the work station from the lane/row selected by an operator on the HMI screen.
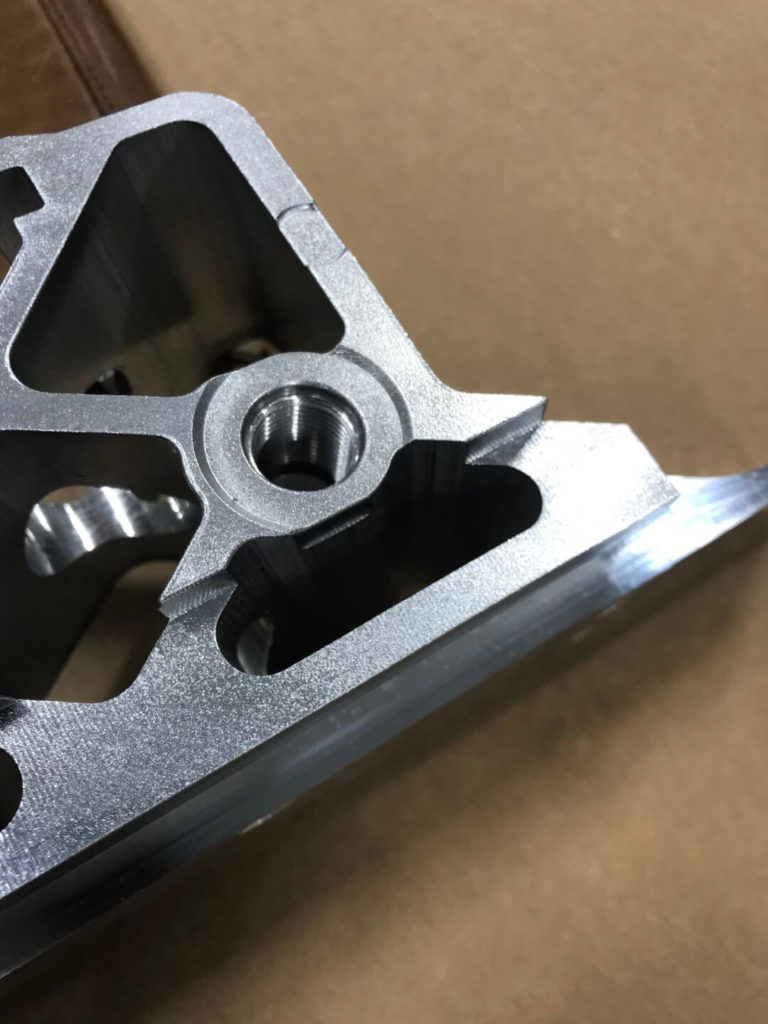
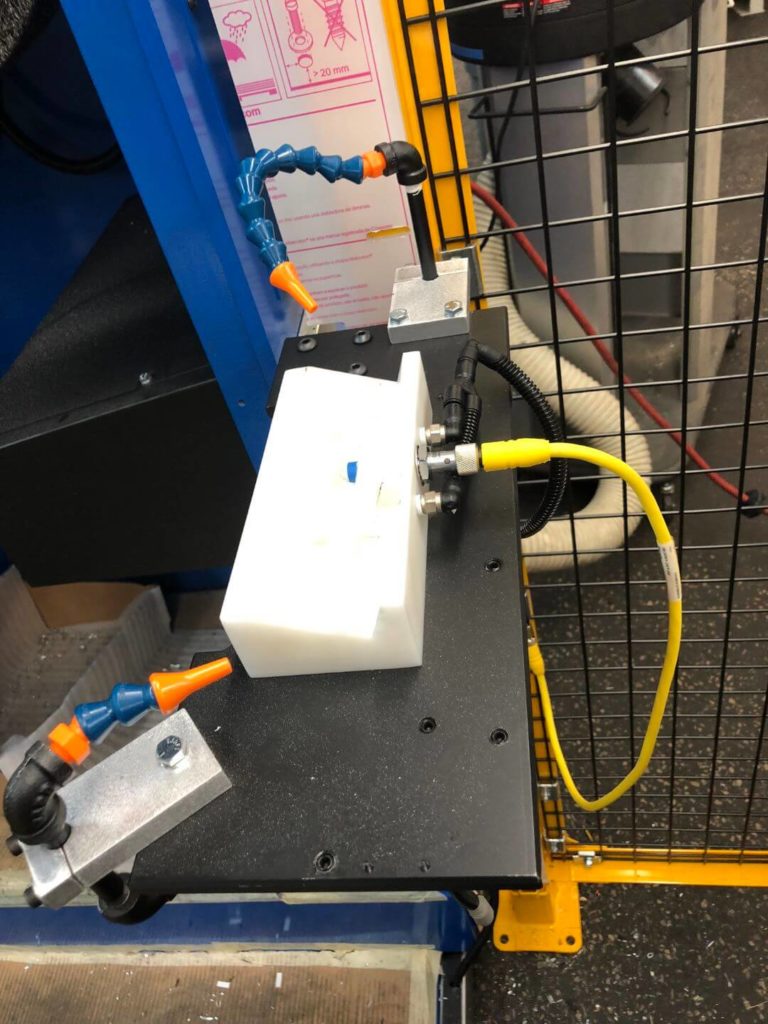
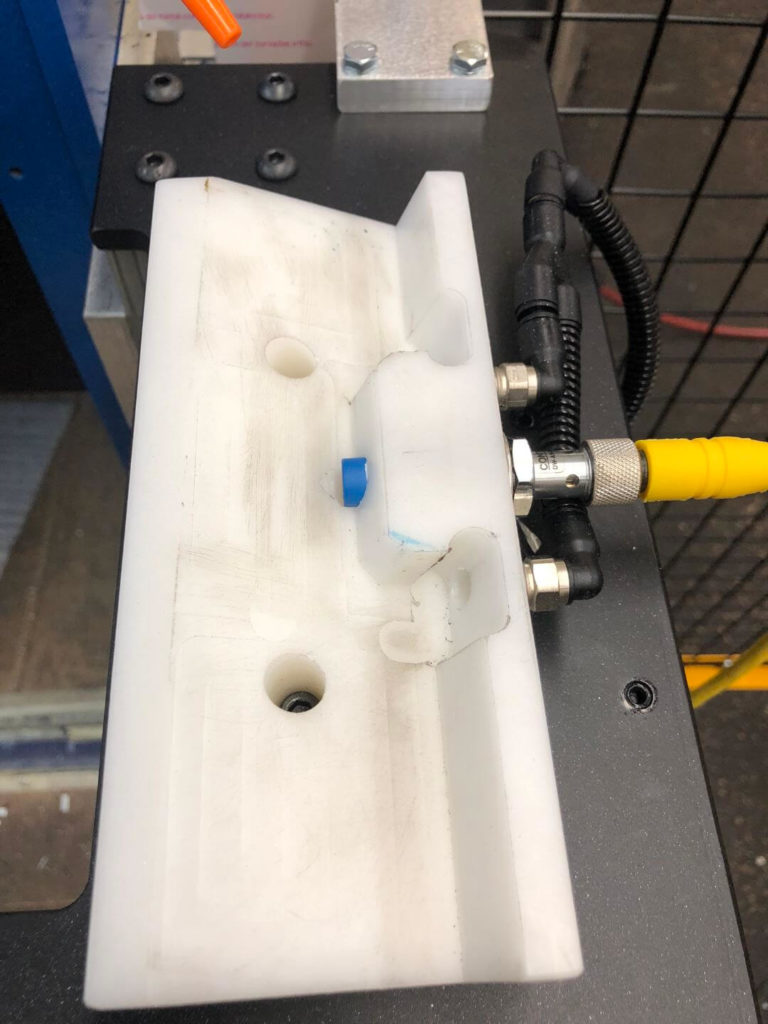
- Due to the clamp surface also being a work surface, the robot must then place the bracket in a custom nest made from acetal resin. While in this nest, a blow-off cleans the part of debris to ensure a consistent regrip. The robot changes position and regrips the part with an alternative EOAT.
- The robot moves to a common work position and proceeds to one of three available ops.
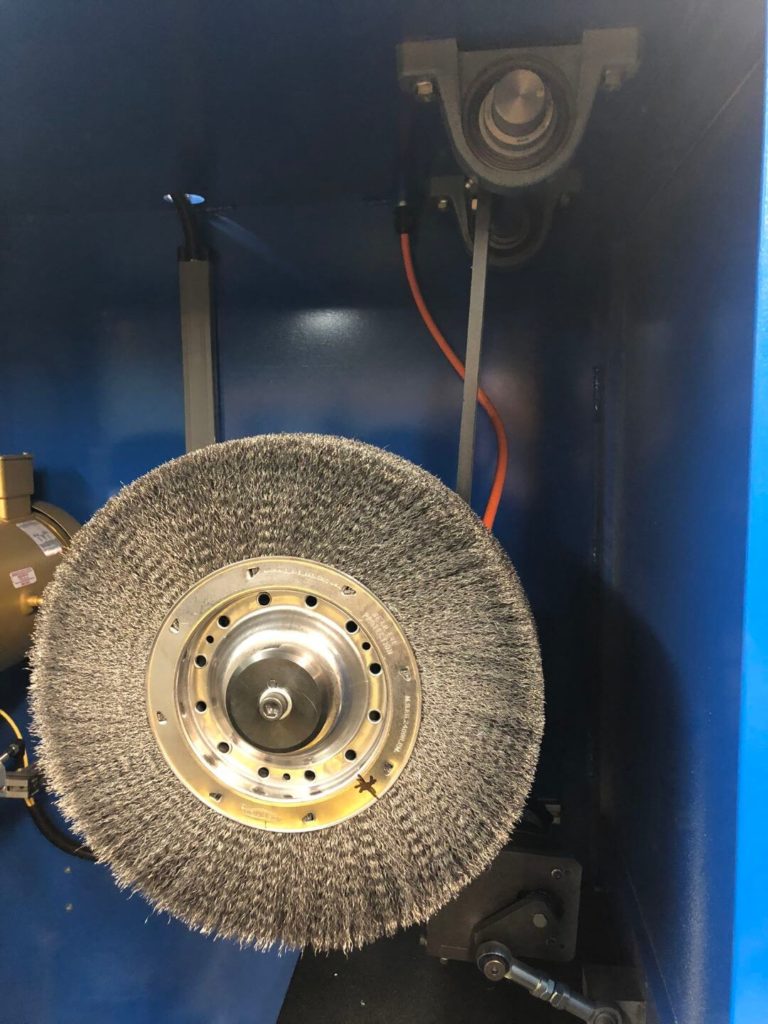
- A 14” crimped steel wire radial brush driven by a large frame D.C. motor is used to cut into one of the burr locations. This stationary assembly cuts in both directions while the robot moves the work piece into it as necessary. Amperage feedback is relayed to the robot so that offsets can be used to adjust cut aggressiveness (Auto Amp Compensation).
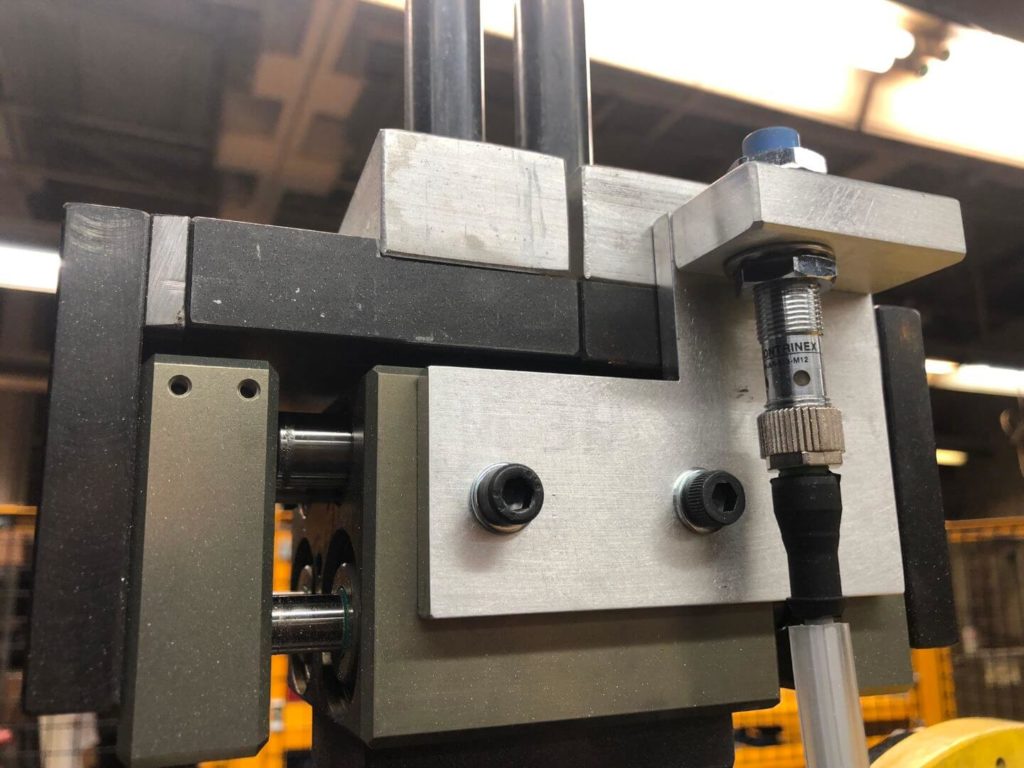
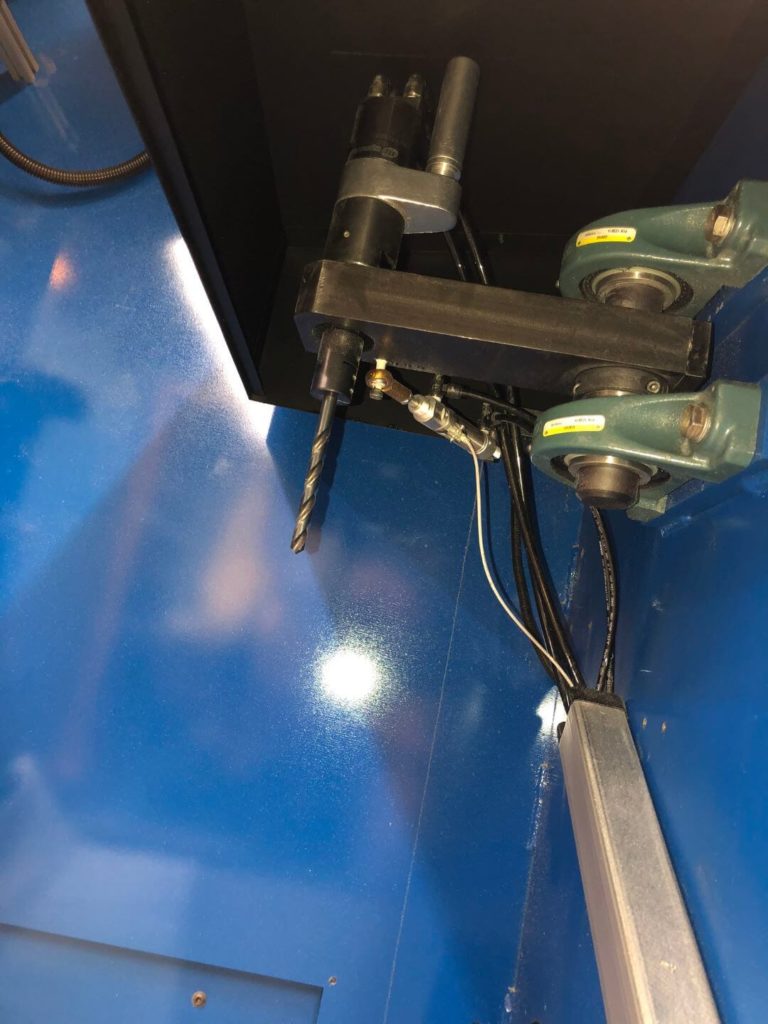
- A drill bit driven by a high rpm air motor is used to pull out residual material from inside the bracket’s corner webs. This air motor is held on a pivot by a small pneumatic cylinder. The robot brings the area to be treated into the drill bit and gently pulls against it, allowing loose material to be pulled away. Cut pressure is adjustable via precision regulator.
- Two directly driven 15” half-twist/crimped wire steel radial brushes are passed through by the robot/work piece. These brush assemblies are attached to a pivot motor, allowing them to utilize Auto Amp Compensation. The bracket is passed through in multiple positions to address various areas of concern.
- Once a work cycle is complete, parts are placed on a large stainless steel washing machine provided to CDMC by WALSH MANUFACTURING. We have worked with WALSH for many years and rely on them for most custom washing solutions.
Safety Implementations
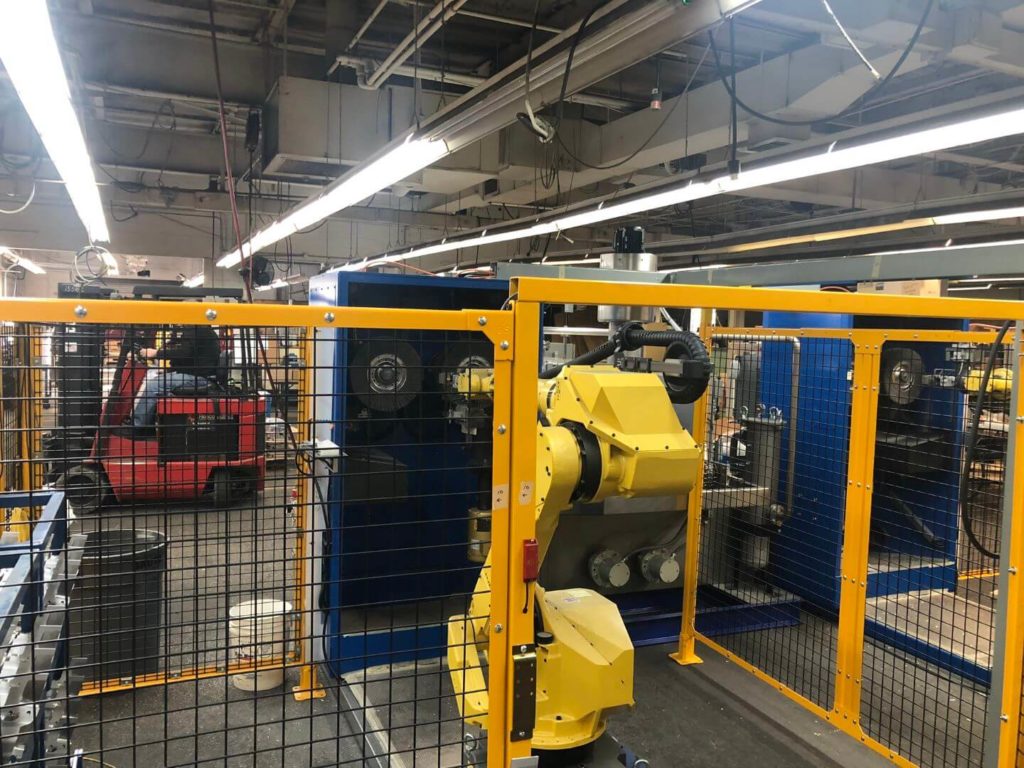
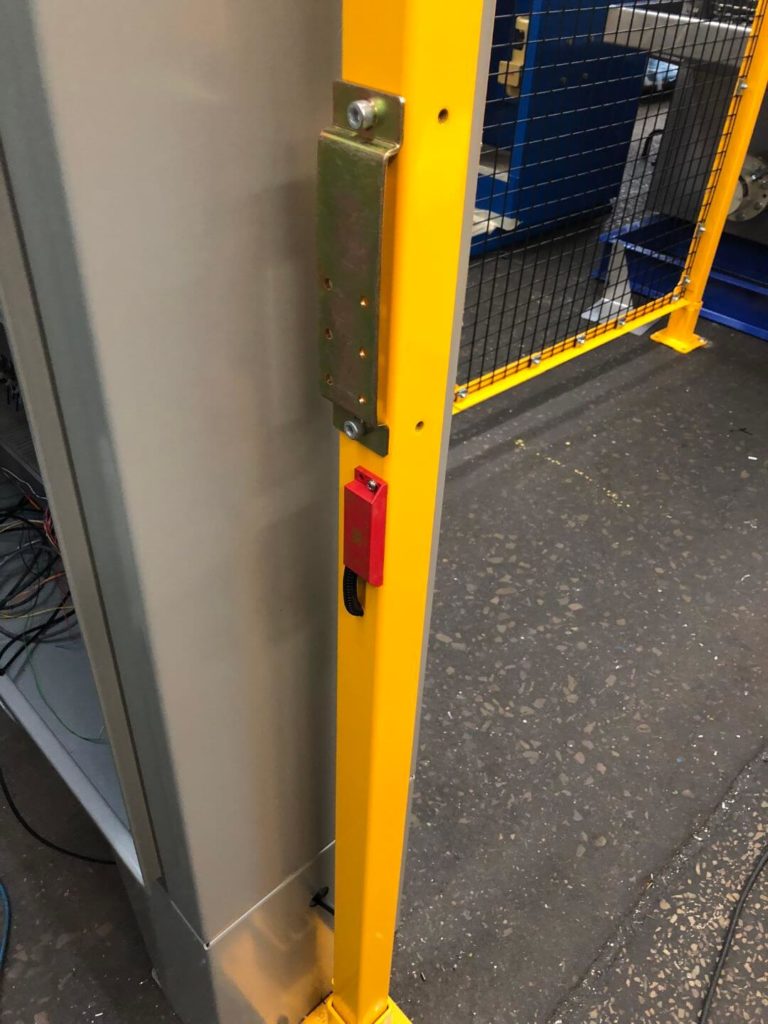
A safety fence is constructed by CDMC to enclose the work area. All manual doors are protected by electronic safety interlocks. If a manual door is opened while a work cycle is active, the machine will stop/enter a fault state immediately.










Results







